
Experiment with oridonin type has demonstrated its antiproliferative effect against leukemia-derived Jurkat cells. A diterpene alkaloid isolated from the Caribbean sponge Agelas citrina has shown antifungal function.
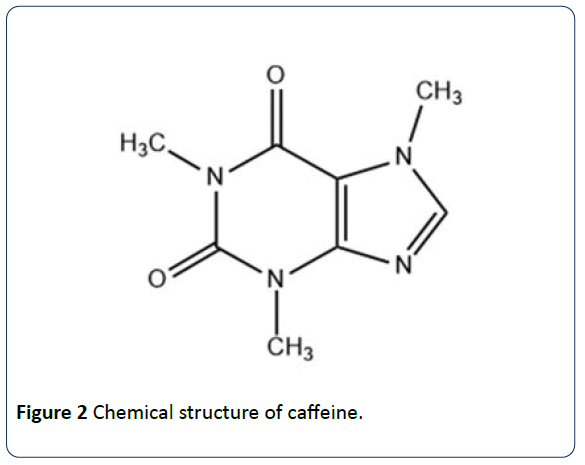
ĭiterpenes have displayed several types of bioactivities via different mechanisms. Some types have been isolated from the fungus Trichoderma longibrachiatum and from sponge family. These and several others may be found in coffee, tea, and Salvia spp. They often occur in a C-20 backbone where isoprene units combine in different forms to give an array of diterpenes such as abietane, cembrane, guanacastepene A, quinonoid, jatropha, and cafestol and kahweol types. ĭiterpenes are a group of terpenoids commonly found as secondary metabolites in terrestrial and marine organisms. Withdrawal from caffeine ingestion may present with lower mental alertness, diminished performance, and over sleepiness. Some of the adverse effects of high doses of caffeine include decrease tonus of the lower esophageal sphincter muscle, overstimulation of central nervous system, intrauterine growth retardation, and higher risk of miscarriage. Investigations have revealed that crude caffeine did possess hydrophilic antioxidant activity (145 μmol Trolox equivalent (TE)/g) and lipophilic antioxidant activity (66 μmol TE/g), and its administration has led to the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme better than aspirin. In a mouse model, crude caffeine was found to reduce the accumulation of β-amyloid peptides, a characteristic feature in patients suffering from Parkinson's disease. Its stimulatory activity was also tested, with some promising results, in persons with Parkinson's disease, where it can be used to manage both motor and nonmotor symptoms. At a dose of 6 mgKg −1 body mass, it was found to exhibit ergogenic effect, the ability to increase physical exercise without a concomitant increase in effort sensation, in sedentary men. It is, therefore, the aim of this paper to present a review on the recent analytical methods that have been applied to the characterization and quantification of four important bioactive constituents in coffee: caffeine, chlorogenic acid, diterpenes, and trigonelline.Ĭonsumption of caffeine has shown many positive effects in various human and animal experimentations. Since the variability of these chemical constituents affects price of coffee commodities by determining their qualities, there must be sensitive, precise, and accurate analytical means for their determination. Coffee contains mineral ingredients such as Ca, K, Fe, P, Ni, Mg, and Cr, polyphenols, caffeine, melanoidins, and carbohydrates among others. There are many nutritive substances in coffee brews which vary with the types of techniques employed in brewing processes. World prices of coffee beans vary reasonably with their geographical source, as this affects the physical presentation of these beans and their nutritive components, two factors that are important in determination of coffee quality. Unfortunately, market shocks, extreme weather conditions, and pests are an enormous challenge to this reality. Presently, the largest coffee bean producing region is Latin America, leading to an immense boost in the economy of the respective countries by bringing in the much needed foreign exchange. It can now be found in both organic and conventional types. However, Coffea canephora and Coffea arabica are the two most economically important species. Coffee is often produced from the roasted beans of a great variety of coffee crops. Since its introduction into Arabia from Ethiopia many centuries ago, its cultivation has continued to blossom in three regions of our globe, namely, Africa, Latin America and Asia. Coffee is a popular beverage that is widely consumed around the world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
